Machine Learning Robustness Study
Within the broader computer vision community, the issue of dataset size has received surprisingly little attention. Most analyses simply use all available data and focus on model architecture, with scant attention given to whether the dataset size is appropriate for the task and architecture’s complexity.
Many different variables determine the ultimate mission impact of satellite imagery, a concept CosmiQ has referred to as the Satellite Utility Manifold. Previous CosmiQ studies have explored such variables as sensor resolution (0.3 meter to 2.4 meter), super-resolution techniques, and the number of imaging bands (grayscale versus multispectral).
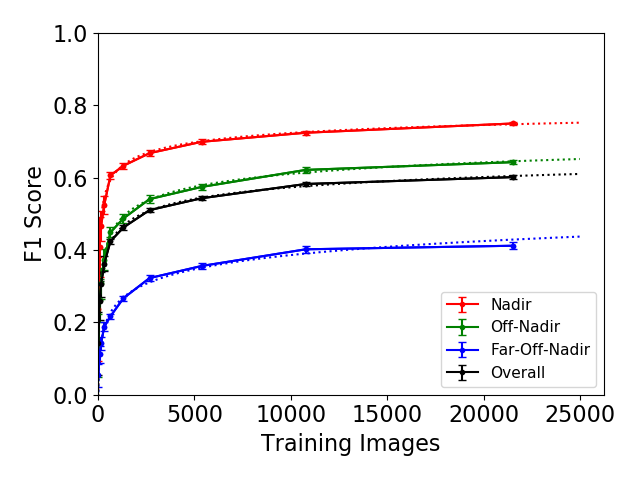
Expanding on this work, the Machine Learning Robustness Study focuses on training dataset size and diversity on building detection performance in the SpaceNet data. The recent availability of this extensive dataset and model-building capability will make it possible to address dependence on geography and dataset size at the leading edge of geospatial machine learning.