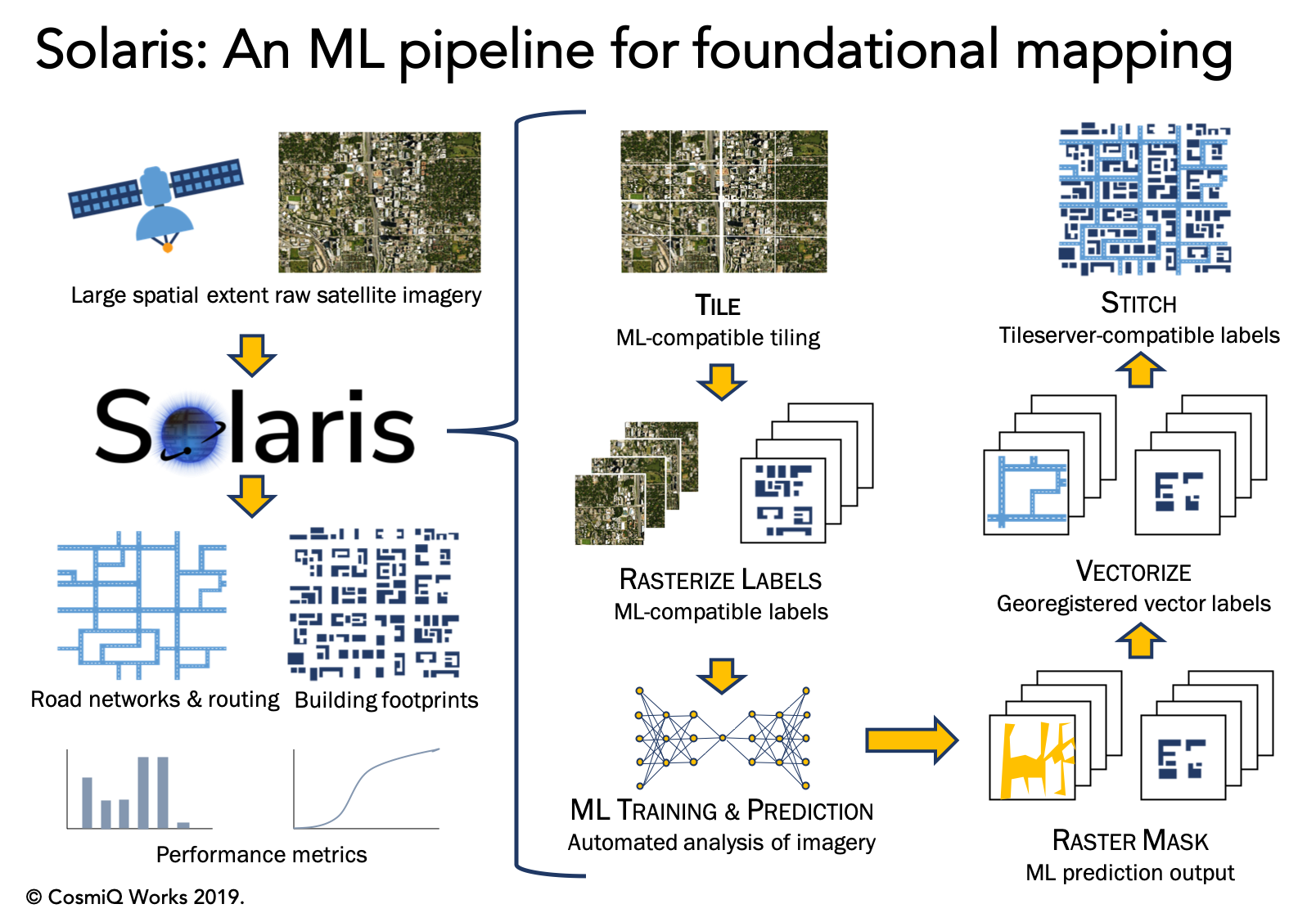
City-Scale Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery (CRESI)
Rapidly extracts large scale road networks and identifies speed limits and route travel times for each roadway
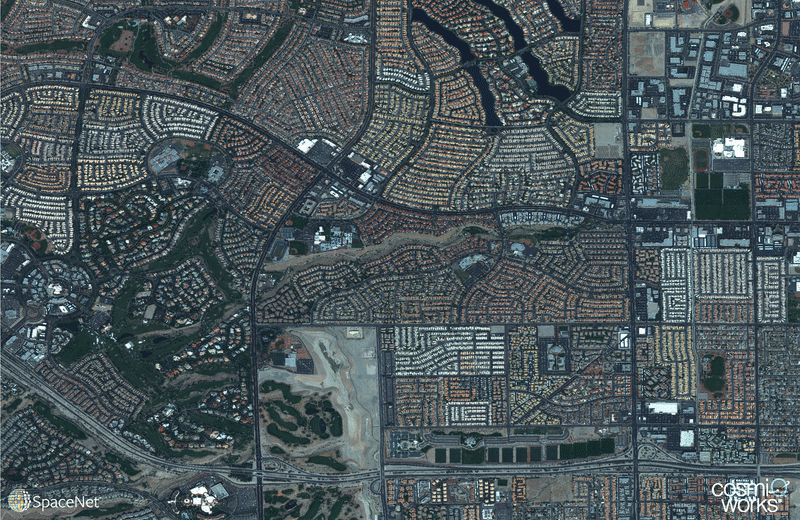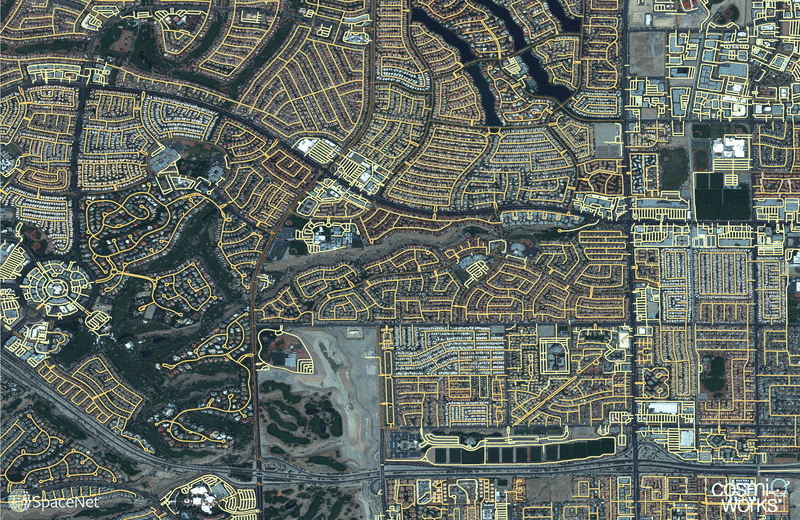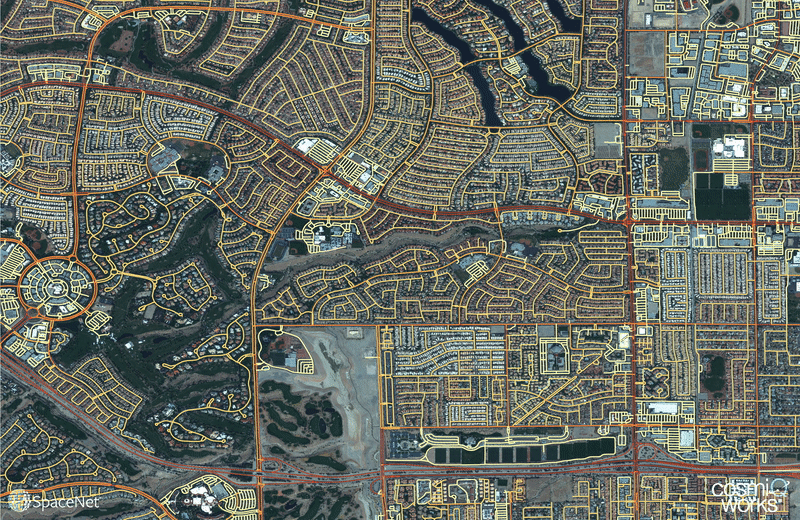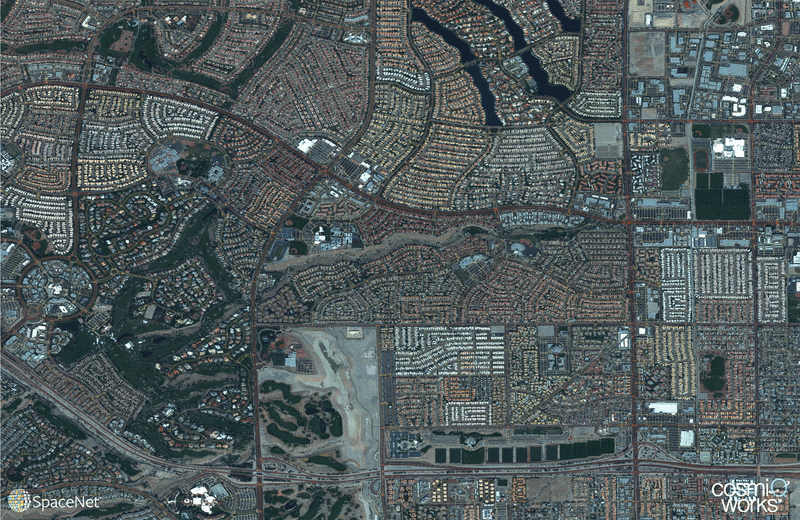 Optimized routing is crucial to a number of challenges, from humanitarian to military. Satellite imagery may aid greatly in determining efficient routes, particularly in cases involving natural disasters or other dynamic events where the high revisit rate of satellites may be able to provide updates far more quickly than terrestrial methods. Existing data collection methods such as manual road labeling or aggregation of mobile GPS tracks are currently insufficient to properly capture either underserved regions (due to infrequent data collection), or the dynamic changes inherent to road networks in rapidly changing environments.
Optimized routing is crucial to a number of challenges, from humanitarian to military. Satellite imagery may aid greatly in determining efficient routes, particularly in cases involving natural disasters or other dynamic events where the high revisit rate of satellites may be able to provide updates far more quickly than terrestrial methods. Existing data collection methods such as manual road labeling or aggregation of mobile GPS tracks are currently insufficient to properly capture either underserved regions (due to infrequent data collection), or the dynamic changes inherent to road networks in rapidly changing environments.
Our City-Scale Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery (CRESI) algorithm served as the baseline for SpaceNet 5, and rapidly extracts large scale road networks and identifies speed limits and route travel times for each roadway. Including estimates for travel time permits true optimal routing (rather than just the shortest geographic distance), which is not possible with existing remote sensing imagery based methods.
Our code is publicly available at github.com/CosmiQ/cresi.